Predictive Models
Moveo One includes a built-in AI engine that converts behavioral data into predictive models — allowing you to anticipate user actions such as drop-off, conversion, or churn.
These models continuously learn from event data and automatically retrain as new patterns emerge.
Predictive models in Moveo One are designed to answer questions like:
- Will the user complete checkout or abandon it?
- What option will user select?
- Will user churn in next X seconds/minutes?
Each model is created around a target event (e.g. checkout_complete) and trained on conditional context (e.g. item_added_to_cart, page_view sequence, or on all events).
Model Lifecycle
- Data Collection — SDKs gather event and session data.
- Model Training — Moveo One backend automatically trains models on aggregated datasets.
- Validation & Scoring — Models are scored for accuracy, recall, and stability.
- Deployment — Once validated, the model becomes active for real-time inference.
- Monitoring — Models continuously adapt as new user behavior data arrives.
Example Model UI
Example internal representation (for illustration only):
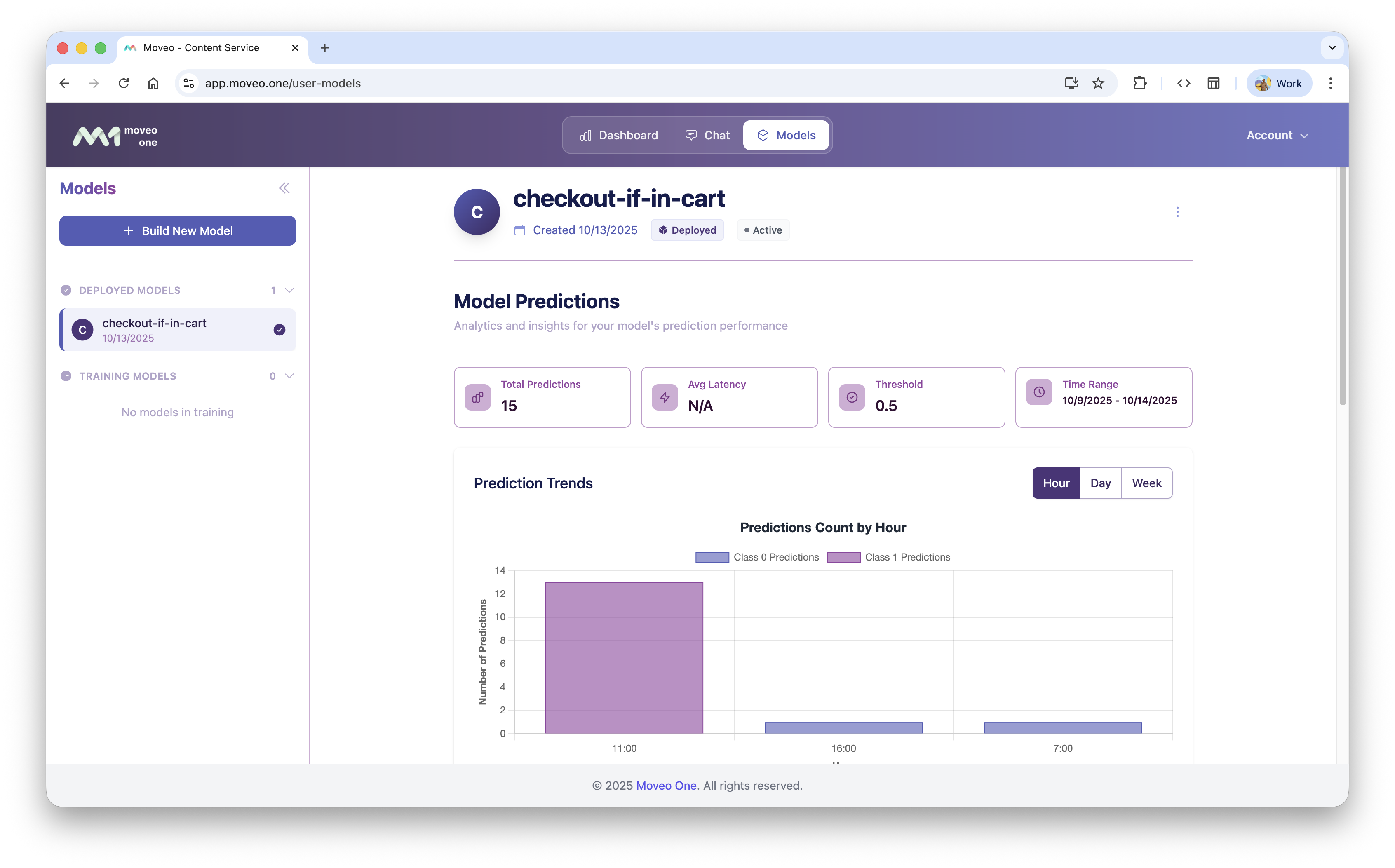
Real-Time Predictions
Once deployed, predictive models can respond to live sessions through the SDKs.
SDK Integration (Client-side)
The MoveoOne SDKs provide a unified predict() method across all platforms to get real-time predictions from your trained models using the current user's session data.
Prerequisites
Before using the predict method, ensure:
- Session is started: Call
start()before making predictions - Valid token: The MoveoOne instance must be initialized with a valid API token
- Model access: Your token must have access to the specified model
- Web
- iOS
- Android
- Flutter
- React Native
Web (JavaScript)
// Get prediction from a model
const result = await MoveoOne.predict("your-model-id");
if (result.success) {
console.log("Prediction probability:", result.prediction_probability);
console.log("Binary result:", result.prediction_binary);
} else {
console.log("Status:", result.status);
console.log("Message:", result.message);
}
iOS (Swift)
// Get prediction from a model
let result = await MoveoOne.instance.predict(modelId: "your-model-id")
switch result {
case .success(let response):
if response.success {
print("Prediction probability: \(response.prediction_probability ?? 0.0)")
print("Binary result: \(response.prediction_binary ?? false)")
} else {
print("Error: \(response.message ?? "Unknown error")")
}
case .failure(let error):
print("Network error: \(error)")
}
Android (Kotlin)
// Get prediction from a model
MoveoOne.getInstance().predict("your-model-id")
.thenAccept { result ->
if (result.isSuccess()) {
val probability = result.getPredictionProbability()
val binaryResult = result.getPredictionBinary()
Log.d("Prediction", "Probability: $probability")
Log.d("Prediction", "Binary result: $binaryResult")
} else {
Log.e("Prediction", "Error: ${result.getMessage()}")
}
}
.exceptionally { throwable ->
Log.e("Prediction", "Unexpected error: ${throwable.message}")
null
}
Flutter
// Get prediction from a model
final result = await MoveoOne().predict("your-model-id");
if (result.success) {
print("Prediction probability: ${result.predictionProbability}");
print("Binary result: ${result.predictionBinary}");
} else {
print("Error: ${result.message}");
}
React Native
// Get prediction from a model
const result = await moveoInstance.predict("your-model-id");
if (result.success) {
console.log("Prediction probability:", result.prediction_probability);
console.log("Binary result:", result.prediction_binary);
} else {
console.log("Error:", result.message);
}
Prediction Response Format
All SDKs return a consistent response format for prediction requests:
Successful Prediction
{
"success": true,
"status": "success",
"prediction_probability": 0.85,
"prediction_binary": true,
"message": null
}
Error Responses
Pending Model Loading
{
"success": false,
"status": "pending",
"message": "Model is loading"
}
Invalid Model ID
{
"success": false,
"status": "invalid_model_id",
"message": "Model ID is required and must be a non-empty string"
}
Not Initialized
{
"success": false,
"status": "not_initialized",
"message": "MoveoOne must be initialized with a valid token before using predict method"
}
No Session Started
{
"success": false,
"status": "no_session",
"message": "Session must be started before making predictions. Call start() method first."
}
Model Not Found
{
"success": false,
"status": "not_found",
"message": "Model not found or not accessible"
}
Conflict (Conditional Event Not Found)
{
"success": false,
"status": "conflict",
"message": "Conditional event not found"
}
Target Already Reached
{
"success": false,
"status": "target_already_reached",
"message": "Completion target already reached - prediction not applicable"
}
Server Error
{
"success": false,
"status": "server_error",
"message": "Server error processing prediction request"
}
Network Error
{
"success": false,
"status": "network_error",
"message": "Network error - please check your connection"
}
Request Timeout
{
"success": false,
"status": "timeout",
"message": "Request timed out after 500ms"
}
A/B Test Control
{
"success": false,
"status": "ab_test_control",
"message": "Prediction skipped due to A/B test configuration"
}
Note: Based on the configuration selected during model training, some portion of sessions will be skipped in order to conduct A/B testing of model effects and performance. When a session is assigned to the control group, the prediction request will return this status code (412) with the ab_test_control status, indicating that the prediction was intentionally skipped for A/B test purposes.
Latency Tracking
All SDKs include built-in latency tracking for prediction requests. This feature helps monitor model performance and identify optimization opportunities.
Key Features
- Automatic latency measurement for all prediction requests
- Asynchronous data transmission (doesn't affect prediction response time)
- Tracks all scenarios including successful predictions and error cases
- Configurable via platform-specific methods
Platform-Specific Configuration
- Web
- iOS
- Android
- Flutter
- React Native
JavaScript/Web
// Enable latency tracking (default: true)
moveoOne.calculateLatency(true);
// Disable latency tracking
moveoOne.calculateLatency(false);
iOS (Swift)
// Enable latency tracking (default: true)
MoveoOne.instance.calculateLatency(enabled: true)
// Disable latency tracking
MoveoOne.instance.calculateLatency(enabled: false)
Android (Kotlin)
// Enable latency tracking (default: true)
MoveoOne.getInstance().calculateLatency(true)
// Disable latency tracking
MoveoOne.getInstance().calculateLatency(false)
Flutter
// Enable latency calculation (default: true)
MoveoOne().calculateLatency(true);
// Disable latency calculation
MoveoOne().calculateLatency(false);
React Native
// Enable latency tracking (default: true)
moveoInstance.calculateLatency(true);
// Disable latency tracking
moveoInstance.calculateLatency(false);
Advanced Usage Examples
Personalized Recommendations
- Web
- iOS
- Android
- Flutter
- React Native
JavaScript
async function getPersonalizedRecommendations(userId) {
try {
const prediction = await MoveoOne.predict(`recommendation-model-${userId}`);
if (prediction.success) {
if (prediction.prediction_binary) {
return {
showRecommendations: true,
confidence: prediction.prediction_probability
};
} else {
return {
showRecommendations: false,
reason: "Low confidence prediction"
};
}
} else {
console.log(`Prediction status: ${prediction.status}`);
return {
showRecommendations: false,
reason: `Prediction not available: ${prediction.message}`
};
}
} catch (error) {
console.error("Unexpected error during prediction:", error);
return null;
}
}
Swift
func getPersonalizedRecommendations(userId: String) async -> [String: Any]? {
do {
let result = await MoveoOne.instance.predict(modelId: "recommendation-model-\(userId)")
switch result {
case .success(let response):
if response.success {
if response.prediction_binary == true {
return [
"showRecommendations": true,
"confidence": response.prediction_probability ?? 0.0
]
} else {
return [
"showRecommendations": false,
"reason": "Low confidence prediction"
]
}
} else {
print("Prediction status: \(response.status ?? "unknown")")
return [
"showRecommendations": false,
"reason": "Prediction not available: \(response.message ?? "Unknown error")"
]
}
case .failure(let error):
print("Unexpected error during prediction: \(error)")
return nil
}
} catch {
print("Unexpected error during prediction: \(error)")
return nil
}
}
Android (Kotlin)
fun getPersonalizedRecommendations(userId: String): CompletableFuture<Map<String, Any>?> {
return MoveoOne.getInstance().predict("recommendation-model-$userId")
.thenApply { result ->
if (result.isSuccess()) {
if (result.getPredictionBinary() == true) {
mapOf(
"showRecommendations" to true,
"confidence" to (result.getPredictionProbability() ?: 0.0)
)
} else {
mapOf(
"showRecommendations" to false,
"reason" to "Low confidence prediction"
)
}
} else {
Log.e("Prediction", "Prediction failed: ${result.getMessage()}")
null
}
}
.exceptionally { throwable ->
Log.e("Prediction", "Unexpected error during prediction: ${throwable.message}")
null
}
}
Flutter
Future<Map<String, dynamic>?> getPersonalizedRecommendations(String userId) async {
try {
final prediction = await MoveoOne().predict("recommendation-model-$userId");
if (prediction.success) {
if (prediction.predictionBinary) {
return {
"showRecommendations": true,
"confidence": prediction.predictionProbability
};
} else {
return {
"showRecommendations": false,
"reason": "Low confidence prediction"
};
}
} else {
print("Prediction failed: ${prediction.message}");
return null;
}
} catch (error) {
print("Unexpected error during prediction: $error");
return null;
}
}
React Native
async function getPersonalizedRecommendations(userId) {
try {
const prediction = await moveoInstance.predict(`recommendation-model-${userId}`);
if (prediction.success) {
if (prediction.prediction_binary) {
return {
showRecommendations: true,
confidence: prediction.prediction_probability
};
} else {
return {
showRecommendations: false,
reason: "Low confidence prediction"
};
}
} else {
console.log(`Prediction status: ${prediction.status}`);
return {
showRecommendations: false,
reason: `Prediction not available: ${prediction.message}`
};
}
} catch (error) {
console.error("Unexpected error during prediction:", error);
return null;
}
}
Checkout Completion Prediction
- Web
- iOS
- Android
- Flutter
- React Native
JavaScript
async function shouldShowCheckoutIncentive() {
try {
const result = await MoveoOne.predict("checkout-completion-model");
if (result.success) {
// Show incentive if probability is below 70%
return (result.prediction_probability ?? 1.0) < 0.7;
} else {
// Default to showing incentive on error
return true;
}
} catch (error) {
return true;
}
}
Swift
func shouldShowCheckoutIncentive() async -> Bool {
do {
let result = await MoveoOne.instance.predict(modelId: "checkout-completion-model")
switch result {
case .success(let response):
if response.success {
// Show incentive if probability is below 70%
return response.prediction_probability ?? 1.0 < 0.7
} else {
// Default to showing incentive on error
return true
}
case .failure(_):
return true
}
} catch {
return true
}
}
Android (Kotlin)
fun shouldShowCheckoutIncentive(): CompletableFuture<Boolean> {
return MoveoOne.getInstance().predict("checkout-completion-model")
.thenApply { result ->
if (result.isSuccess()) {
// Show incentive if probability is below 70%
(result.getPredictionProbability() ?: 1.0) < 0.7
} else {
// Default to showing incentive on error
true
}
}
.exceptionally {
true
}
}
Flutter
Future<bool> shouldShowCheckoutIncentive() async {
try {
final result = await MoveoOne().predict("checkout-completion-model");
if (result.success) {
// Show incentive if probability is below 70%
return (result.predictionProbability ?? 1.0) < 0.7;
} else {
// Default to showing incentive on error
return true;
}
} catch (error) {
return true;
}
}
React Native
async function shouldShowCheckoutIncentive() {
try {
const result = await moveoInstance.predict("checkout-completion-model");
if (result.success) {
// Show incentive if probability is below 70%
return (result.prediction_probability ?? 1.0) < 0.7;
} else {
// Default to showing incentive on error
return true;
}
} catch (error) {
return true;
}
}
Important Notes
Performance & Reliability
- The
predict()method is non-blocking and won't affect your application's performance - All requests have a 500ms timeout (except Flutter which uses 5 seconds) to prevent hanging
- The method automatically uses the current session ID and sends all buffered events to the prediction service
- Active session required - Make sure to call
start()before using predict method
Response Handling
- Always check
success: truefor complete predictions predictionProbabilityandpredictionBinaryare optional - they will benullfor error responses- Handle all error states gracefully, including pending states
- Use appropriate timeout handling for your platform
Best Practices
- Initialize properly: Always initialize MoveoOne with a valid token before use
- Start sessions: Call
start()before making predictions - Handle errors: Implement proper error handling for all response states
- Monitor performance: Use latency tracking to monitor prediction performance
- Test thoroughly: Test prediction flows in different network conditions
Accuracy & Monitoring
Each model’s quality is continuously monitored using:
- Precision / Recall
- F1-score
- Temporal drift analysis
- Feature relevance tracking
You can view performance graphs in the Moveo One dashboard under AI → Predictive Models.
Building Custom Models
Moveo One also supports building your own models directly from the dashboard.
Example workflow:
- Select a Target Event (e.g.,
checkout_complete) - Choose Conditional Events (e.g.,
add_to_cart,view_product) - Define Observation Window (e.g., 30 minutes before target event)
- Click Build Model
The backend automatically:
- Extracts relevant features
- Splits data into train/test sets
- Tunes hyperparameters
- Deploys the model to production
Best Practices
✅ Recommended
- Use meaningful target events (e.g.,
purchase_complete, notbutton_click) - Retrain models after major UX changes
- Compare prediction distributions pre/post feature release
❌ Avoid
- Training on rare or one-time events
- Mixing unrelated behaviors in one model
- Ignoring feature drift over time